Automatic recycling of flat screens
PDF - 2 218 ko

Our environment and our climate are based on a very delicate balance, which high-quality recycling of electrical and electronic equipment (EEE) helps to preserve.
First and foremost, equipment decontamination helps to protect health and ecosystems, by extracting and eliminating pollutants. By also destroying the refrigerant and insulating gases found in refrigerators, for example, it makes an effective contribution to the fight against global warming. EEE recycling then goes through successive phases of separation and purification of the materials making up the equipment, until they are recovered and reintegrated into new products: these are the recycled materials.
To integrate the challenges of recycling a product right from the design phase, we need to understand how it will be recycled.
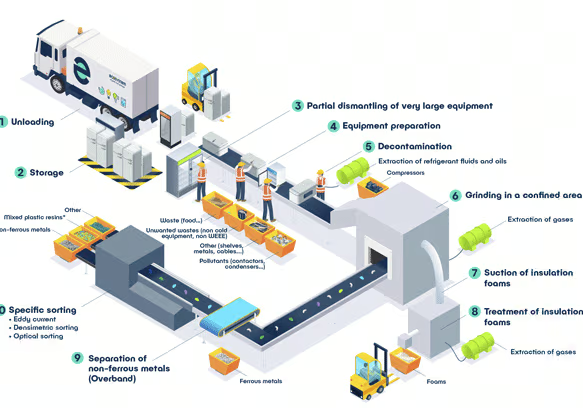
Electrical and electronic equipment is recycled as a mixture at treatment sites, where pollutants are removed and its materials separated. But not all equipment can be recycled together! Depending on their size and the presence of pollutants, electrical equipment goes into specific WEEE streams.
Take a step-by-step look at the recycling process for different types of equipment, using the diagrams below!
Automatic recycling of flat screens
PDF - 2 218 ko
Manual recycling of flat screens
PDF - 1 908 ko
Recycling cathode-ray tubes screens (CRT screens)
PDF - 2 496 ko
Recycling fluorescent tubes
PDF - 3 034 ko
Recycling lamps
PDF - 6 376 ko
Recycling large appliances excluding cold
PDF - 3 868 ko
Recycling large cold appliances
PDF - 2 126 ko
Recycling plastics
PDF - 5 077 ko
Recycling small electrical and electronic appliances
PDF - 3 226 ko
The type of recycling currently involving equipment for which ecosystem is accredited is mostly mechanical. Mechanical recycling involves the transformation of waste using machines and physical-mechanical processes. It should be distinguished from chemical recycling. To find out more about the development of chemical recycling and its applicability to WEEE, discover this study in French: